In this article, I am going to show you how to build a super large, ultra reliable, expandable file server with mixed size of hard drives.
Here is my criteria:
- Large Storage Capacity. At this moment, the largest hard drive is 2TB. I am looking for at least 10TB.
- Great Performance. The users should not feel any delay when multiple users are reading/writing to the file server at the same time.
- Reliable. No data loss or inconsistent. The file system should repair by itself.
- Expandable. The file system must be expandable. During the upgrade, the data should be preserved (i.e., don’t need to wipe out the original data)
- Client Independent / Cross Platform. The user should be able to access the file server from any OS.
- Software based / Hardware Independent. In case of hardware failure, it will be easy to transfer the entire system to a different computer.
I am going to show you how to implement all of these using FreeBSD and ZFS. The idea of the implementation is the same on other operating systems that support ZFS, such as *Solaris, *BSD etc. However, using ZFS on Linux (via Linux FUSE) is not recommended given the performance / stability issues (See Wikipedia for details). I personally do not recommend running ZFS on Linux in production environment.
Before I talk about how I do it, I like to go over what other technologies I tried before, and why they are not qualified.
RAID + LVM on Linux
This is one of the most common techniques used by many people on building file server. First, you need to build a RAID device using mdadm on the selected harddrives with identical size. If you have different size of harddrive, you will need to put them on a separated RAID device because mdadm does not support mixing different size of harddrive in a single RAID device without losing usable space. Later, you combine multiple devices (RAID, single harddrives etc) into a single partition using LVM.
The good thing about this technique is the expandability, i.e., you can add any hard drive to the partition at any time without losing any data at any time. However, there are few disadvantages of this combination:
Poor reliability
The reliability is handled at the RAID level. If your setup is not 100% RAID, such as the following example, the reliability can be discounted.
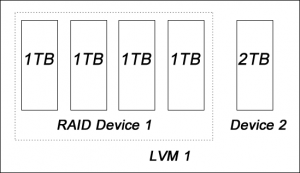
In this example, if the device 2 (2TB) is failed, the data that is stored on device 2 will be lost, because the data redundancy is only available on device 1.
Performance is not optimized
Data redundancy helps to improve the performance especially on reading. Again, if the setup is not one single RAID device, the performance can be discounted too.
So, let’s see how ZFS can solve these issues.
ZFS
ZFS is the next generation file system developed by Sun. It comes with all advantages of mdadm + LVM, plus a lot of features such as compression, encryption, power failure handling, checksum etc. So why this setup is better than the LVM one? Let’s take a look to the following example:
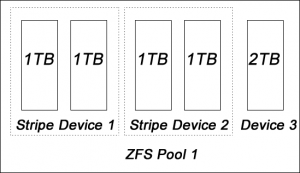
In this example, all devices in the ZFS pool are protected against data failure.
Let’s Start Building A Super Large File Server Now!
First, let’s assume that I have the following hardware:
- A 64-bit system with at least 2GB memory. Although ZFS will do fine on 32-bit system with 512MB memory, I recommend going with higher configurations because ZFS uses a lot of resources. In my case, I use an AMD Dual Core 4600+ (manufactured in 2006) with 3GB memory.
- Mixed size of harddrives, the size of the larger harddrive has to be divisible by the smaller one. In my case, I have 2TB and 1TB harddrives. Keep in mind that 2x1TB = 2TB.
- The harddrives are connected to the system using IDE/SATA. No firewire or USB.
- Four 1TB harddrives (A, B, C, D)
- Three 2TB harddrives (E, F, G)
- One extra harddrive, any size, reserved for the system uses. (H)
Using this combination(10GB in total), you can build a big file server with 8GB or 6GB, depending on your preference of data security.
I am going to build a RAIDZ2 device using FreeBSD and ZFS. In general ZFS is only available on the harddrives with the same size (without losing harddrive space). Since I want to put my 1TB and 2TB harddrives in the same pool, I first create couple RAID0 drives first. Then I add them together to make a big ZFS device. Here is the big picture:
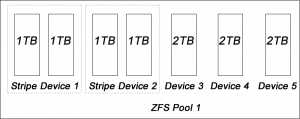
Building RAID0 Devices
As usual, login as root first.
sudo su
And load the stripe module:
kldload geom_stripe
Now we need to create a RAID0 device from /dev/ad1(A: 1TB) and /dev/ad2(B:1TB). If you are unsure about the device name, try running dmesg for details:
dmesg | grep ad
gstripe label -v st0 /dev/ad1 /dev/ad2
And label the new device: /dev/stripe/st0
bsdlabel -wB /dev/stripe/st0
Format the new device:
newfs -U /dev/stripe/st0a
Mount the device for testing:
mount /dev/stripe/st0a /mnt
Verify the size:
df -h
Add the following into /boot/loader.conf:
geom_stripe_load="YES"
Now, reboot your machine. If /dev/stripe/st0 is available, then your RAID0 device is ready.
If you need to build more RAID0 devices, repeat the above steps. Keep in mind that you need to change the device name from st0 to st1.
Putting all devices together into ZFS Pool
First, let’s enable ZFS first:
echo 'zfs_enable="YES"' >> /etc/rc.conf
and start ZFS:
/etc/rc.d/zfs start
Get your devices ready. In my cases, my devices name are:
/dev/ad5: 2TB
/dev/ad6: 2TB
/dev/ad7: 2TB
/dev/stripe/st0: 2TB (RAID0: 2x1TB)
/dev/stripe/st1: 2TB (RAID0: 2x1TB)
Create the ZFS pool, which will mount on /storage/data
Note that I use raidz2 here for extra protection against data failure. Basically, raidz (single parity) allows up to 1 failed harddrives while raidz2 (double parity) allows up to 2 failed harddrives.
- RAIDZ: Usable space: 8GB, allow up to one 2TB harddrive group failed (i.e., one 2TB or two 1TB in the same group)
- RAIDZ2: Usable space: 6GB, allow up to two 2TB harddrive groups failed (i.e., two 2TB or two 1TB in the different groups)
zpool create storage raidz2 /dev/ad5 /dev/ad6 /dev/ad7 /dev/stripe/st0 /dev/stripe/st1
zfs create storage/data
Verify the result:
zpool status
df -h
We need to make some performance tweaking first, otherwise the system will be very unstable. Add the following to the /boot/loader.conf
#Your Physical Memory minus 1 GB
vm.kmem_size="3g"
vm.kmem_size_max="3g"
vfs.zfs.arc_min="512m"
#Your Physical Memory minus 2GB
vfs.zfs.arc_max="2048m"
vfs.zfs.vdev.min_pending="1"
vfs.zfs.vdev.max_pending="1"
Now reboot the system:
reboot
To test the stability of the system, I recommend saving some files into the ZFS pool and run it for few days.
Why Running ZFS on Linux is not a Solution?
ZFS is not supported by Linux natively due to legal issue. In the other words, it is not supported by Linux kernel. Although ZFS has been ported to Linux via FUSE, which is running ZFS as an application, it will introduce the performance and efficiency penalties. (Source: ZFS Wiki). So I don’t recommend running ZFS on Linux.
Enhancement Idea
- You can use Samba to share the files with Windows users.
- To secure your data, I recommend set up another system on a separate machine and mirror the data using rsync.
Further Readings
- FreeBSD Handbook: RAID0 – Striping
- FreeBSD Handbook: The Z File System (ZFS)
- ZFS Tuning Guide
Our sponsors: